Business Continuity methodologies have been around for decades. Business processes, technology, culture, markets, media and communication have all changed – yet BCM is still virtually the same. It shouldn’t surprise anyone that ‘Selling BCM to the C-Suite” is a problem of epidemic proportions. Executives see little – if any – value in current BCM methods and plans. Auditors have progressed beyond accepting BIA compilations and door-stopper BCPs as evidence of BCM compliance. They have a new yardstick: ‘stress-testing’ your ability to respond to disruptions & resume operations against all odds. They are questioning your organization’s ability to continue to deliver critical products & services following any interruption.
That’s the new raison d’être of BCM programs. And as an industry, we’ve been failing to meet that objective. You can no longer simply compile lists of critical resources, build Call Trees and call it a Plan. Auditors and new standards are looking for proof of incident readiness.
What is Incident Readiness? – A program with tested, viable response plans, capable of responding effectively to any disruption – with the proven ability to restore critical assets to ensure continuity of operations.
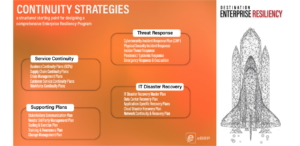
The 3 components of an Incident Ready program are:
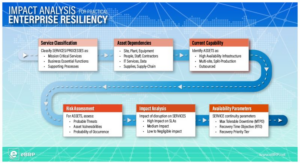
- Planning: Is the entire, typical BCM life cycle – Risk Assessment, BIA, Strategy development, Plan development, testing/exercising and maintenance – for sustainability of the program. It should have an emphasis on identifying critical assets, and the tasks that are needed to restore those assets (not simply locations or departments).
- Incident Response: Is a systematic process to identify the impacts of a disruption and the resulting causality chain. It must also incorporate the decision support framework necessary to craft an effective response.
- Incident Management: Tracks the business objectives, timelines, resources, SLAs, assets, logistics against the relevant aspects of the incident response to ensure both its effectiveness and efficiency. (A well-established standard for Incident Management is the NIMS-ICS framework.)
Only a BCM program, in which program objectives incorporate all three of these components – Planning, Incident Response, and Incident Management – can lead to Incident Readiness. The program need not adhere to linear ‘best practices. By focusing on critical assets (instead of planning for the entire enterprise), planning and response for critical components can be completed and validated independently. You can get off of the BIA carousel. You can avoid Risk Assessment ‘analysis paralysis’, and create plans with clear, concise objectives (not broad, vague one-size-fits-all tomes).
With a goal of Incident Readiness, all components can coexist; there’s no need to complete one component for the entire enterprise before moving on. If you’ve always known there had to be a better way – or if you are simply curious – read part 2 (of this three-part series) focusing on how to achieve Incident Readiness, a value that traditional BCM methods cannot.do.